CUDA Stream
→ Host에서 Device로 명령을 보내는 통로(Host에서 호출하는 명령들이 차례대로 들어감)
Types of CUDA Stream
- NULL stream → 암묵적으로 선언된 stream
- 사용할 stream을 명시하지 않은 경우(default stream)
- Non-NULL stream → 명시적으로 선언된 stream
- 명시적으로 생성 및 사용
하나의 stream에 들어온 명령은 순서대로 Device에 의해 처리된다.
→ Synchronous execution
C() → B() → A()
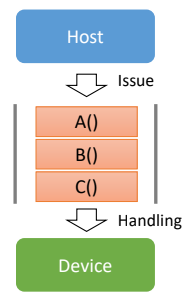
하지만 서로 다른 stream에 있는 명령들은 순서가 정해져 있지 않다.(비동기적)
즉, stream들이 명시되어 있으면 비동기적인 stream이 될 수 있다.
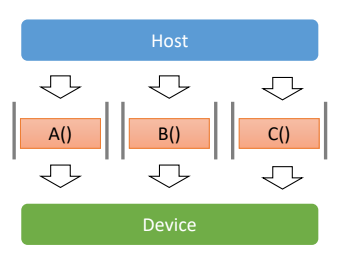
Concurrent Execution
→ 서로 다른 stream에 있는 작업 중 일부는 동시에 수행될 수 있다.
동시에 수행(overlap)이 가능한 작업들
- Host computation and device computation
- Host computation and host-device data transfer
- Device computation and host-device data transfer
- Concurrent device compuatations
* 동시 수행 능력은 GPU마다 다를 수 있다.
동시에 작업이 가능하기 때문에 이를 활용하면 높은 성능을 낼 수 있다.
아래 그림을 살펴보자.
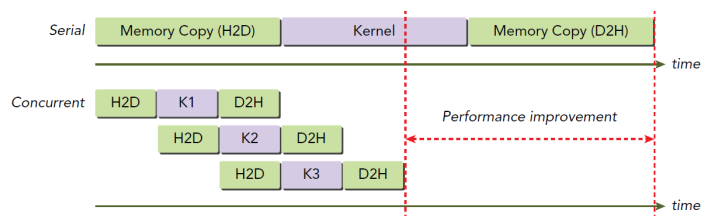
stream을 3개로 나눴을 때 다음과 같이 동시에 작업이 처리될 수 있다.
그렇다면 어떻게 non-NULL Stream을 만드는지 알아보자.
- Create/Destory
- Data type : cudaStream_t
- cudaError_t cudaStreamCreate(cudaStream_t*)
- cudaError_t cudaStreamDestory(cudaStream_t)
|
1
2
3
4
|
cudaStream_t stream;
cudaStreamCreate(&stream);
myKernel<<<dimGrid, dimBlock, 0, stream>>>(...)
cudaStreamDestory(stream);
|
cs |
Synchronous data transfer
|
1
2
|
cudaMemcpy(d_a, a, memSize, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemcpy(b, d_b, memSize, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
|
cs |
Asynchronous data transfer
- Device and Host compuatation과 동시에 수행될 수 있음
- Stream에 명령을 넣은 후, 제어를 바로 반환
- Pinned memory에만 사용 가능
Pinned Memory
- Page-locked memory
- 메모리에 상주하는 Page(Swap-out되지 않는다.)
- Host-device 사이의 Asynchronous data transfer를 위해서는 host memory가 Page-locked상태여야 함
- Data transfer 중 해당 영역이 메모리 상에 존재함이 보장되어야 함
- 속도도 더 빠름
- Pinned memory allocation
- cudaError_t cudaMallocHost(void ** ptr, size_t size)
- cudaError_t cudaFreeHost(void *ptr)
- Asynchronous memory transfer
- cudaError_t cudaMemCpyAsync(void* dst, const void* src, size_t size,
enum cudamemcpyKind, cudaStream_t stream=0)
- cudaError_t cudaMemCpyAsync(void* dst, const void* src, size_t size,
명시적인 Stream Synchronization
- cudaError_t cudaDeviceSynchronize()
- 모든 stream에 대한 synchronization
- cudaError_t cudaStreamSynchronize(cudaStream_t)
- 해당 stream에 대한 synchronization
- cudaError_t cudaStreamQuery(cudaStream_t)
- 해당 stream의 현재 확인
- CudaEvent
암묵적인 Stream Synchronization
다음 operation들 다음에는 암묵적인 barrier가 존재(concurrent execution 불가능)
- A page-locked host memory allocation
- A device memory allocation
- A device memory set
- A memory copy between two addresses to the same device memory
- Any CUDA command to the NULL stream
- A switch between the L1/shared memory configurations
'School Study > Multi Core Programming' 카테고리의 다른 글
| CUDA Event (0) | 2019.05.21 |
|---|---|
| Synchronization in CUDA (0) | 2019.05.21 |
| Maximizing Memory Throughput (0) | 2019.05.14 |
| CUDA Memory Model (0) | 2019.05.07 |
| CUDA Execution Model (0) | 2019.05.07 |



